Blood pulse, cardiac pulse / Pulsations cardiaques
Recognition using the blood pulse shape or the electrocardiogram has been proposed, but there was low activity on this subject until 2013 when a product was announced.
La reconnaissance par la forme du pouls sanguin ou de l'électrocardiogramme a été proposé, mais il n'y avait que peu d'activité dans ce domaine jusqu'en 2013, lorsque qu'un produit a été annoncé.

Pulse reading
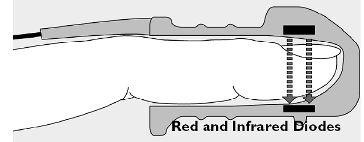
Pulse reading is performed using the same material than pulse oxymetry, with two LEDs and a photodiode, to read the blood pulse shape. One LED is enough if you just want to acquire the blood pulse.


Blood pulse waveform / forme d'onde du pouls
La lecture s'effectue avec le même matériel que pour l'oxymétrie par le pouls, à l'aide de 2 DEL et d'une photodiode. Une seule DEL suffit si vous voulez juste acquérir le pouls.
C'est un appareil relativement facile à réaliser, même moi je l'ai fait à partir de puces du commerce.
Electrocardiogram / ECG / EKG
Everyone knows how a regular EKG is done, using several electrodes, close to the heart.
But the minimum requirement to acquire an EKG is form a loop with the heart, for instance between the two hands. Electrodes at the end of a finger is not enough.
Search for "handheld ECG" for more info.

On connait généralement la manière de réaliser un ECG, avec des électrodes disposées plutôt près du coeur. Mais il faut au minimum 2 électrodes et former une boucle dans le corps, par exemple en utilisant les deux mains. Au bout d'un doigt, il n'y a pratiquement pas de signal.
Wave radar
“Cardiac Scan” is a radar-based system that can identify the exact shape of a heart.
Press release fron Buffalo university
A novel continuous authentication system, namely Cardiac Scan, based on geometric and non-volitional features of the cardiac motion is presented. Cardiac motion is an automatic heart deformation caused by self-excitement of the cardiac muscle, which is unique to each user and is difficult (if not impossible) to counterfeit. Cardiac Scan features intrinsic liveness detection, unobtrusiveness, cost-effectiveness, and high usability. We prototype a remote, high-resolution cardiac motion sensing system based on the smart DC-coupled continuous-wave radar. Fiducial-based invariant identity descriptors of cardiac motion are extracted after the radar signal demodulation.
- (2017) Cardiac Scan: A Non-Contact and Continuous Heart-Based User Authentication System / Chen Song & als.

Laser
MIT Technology Review reports that the Pentagon now has a prototype infrared laser
that can identify people by their heartbeat. It is called “Jetson” and uses laser vibrometry
to detect movements on the surface of the skin caused by a person’s pulse.
It even works from as far as 200 meters away.
There are some caveats though. While the laser can detect a heartbeat from a distance
on bare skin or through thin material like a tee shirt, thicker clothing like a jacket makes
it ineffective. The system also needs about 30 seconds to create a good enough profile
for analysis. The subject must be still during that time as well.
General info
There are many papers related to identification using ECG. Here are some starting papers:
- (2012) ECG Biometric Recognition: A Comparative Analysis / Ikenna Odinaka ; Po-Hsiang Lai ; Alan D. Kaplan ; Joseph A. O'Sullivan ; Erik J. Sirevaag ; John W. Rohrbaugh
- (2015) Electrocardiogram (ECG) as a Biometric Characteristic: A Review / Gaganpreet Kaur, Dr. Dheerendra Singh, Simranjeet Kaur
- (2005) Paper and database / Tatiana LugovayaBiometric human identification based on electrocardiogram. [Master's thesis]
Proposed systems
- (1996) The Klipsh School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, New Mexico State University has published an article:
Use of Blood Pulse Signature for Identity Verification (Ludeman & als) - (2004 Jan) Union Recovery (formerly Tarian 2001) has proposed a blood pulse recognition system, but there is no commercially availble device (US patent 7536557).
- (2011) Unveiling the Biometric Potential of Finger-Based ECG Signals (André Lourenço, Hugo Silva, and Ana Fred): finger-based ECG biometric system. The proposed approach allowed us to obtain a 94,3% recognition rate in subject identification and a 13,0% EER in subject authentication. By applying a user-tuned threshold selection method, authentication results were further improved to a 10,1% EER


- (2014) Embedded system for individual recognition based on ECG Biometrics(André Cigarro Matos, André Lourenço, José Nascimento)
- (2013) Bionym will propose the Nymi, a plastic wristband using a biometric sensor to authenticate identity through a person’s unique electrocardiogram.
Bionym has developed the first wearable authentication device that utilizes
a user's Electrocardiogram (ECG) to validate a person’s identity.
The Nymi has two electrodes, one on the wrist and one on the top.
To authenticate, a user must attach the Nymi, and then place their finger on the top electrode
to complete the electric current.
A user only needs to validate their identity once, until the Nymi is removed.
The closed loop keeps the Nymi in an authenticated state,
removing all need for repeated prompts (such as in fingerprint scanning or PIN requests).
Once authenticated, the Nymi communicates the user’s identity to a device
(such as a smartphone, vehicle, elctronic lock, or even a smart environtment)
using Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE).
The Nymi also has an integrated accelerometer and gyroscope,
which will pick up on your movements, allowing for simple, task-specific gesture recognition.
Motion sensing works in unison with proximity detection and identity authentication
to ensure only you can remotely access the devices you want to engage with.

- (2015) Olea proposes the Olea HeartSignature.
A revolutionary authentication technology which has the ability to accurately and continuously identify individuals in real time with precision comparable to existing biometric authentication systems.
Based on a 5.8GHz Doppler radar sensor. Proposed for car seatbelt.

- (2015) B-Secur proposes an ECG biometric solution. No info about the reader, if any.
- (2016) The patent WO 2016135437 A2 describes a device (a smartcard or the like) with two contacts -one for each finger of each hand, what a surprise!- able to communicate with a smartphone. So, again, something not so practical as it requires an additional device and the two hands to be used... plus the usual security problems to solve linked to the communication.
- (2021) Taliware proposes Biombeat.
Taliware’s biombeat is an API enabling ECG capable smartwatch to deliver identity-as-service (IDaaS) using the latest in biometric and location identifiers --cardiac rhythm based geo authentication.
(2021 March) Taliware Biombeat is currently compatible with Apple Watch models equipped with an ECG sensor.