Skin Properties
Skin properties can be used to recognize persons :
- Light properties :
- Electrical properties :
Skin spectrum / Spectre de la peau
Lumidigm has established that the absorption spectrum of the skin depends on the individuals.
Lumidigm a découvert que le spectre d'absorption de la peau est dépendant des individus.

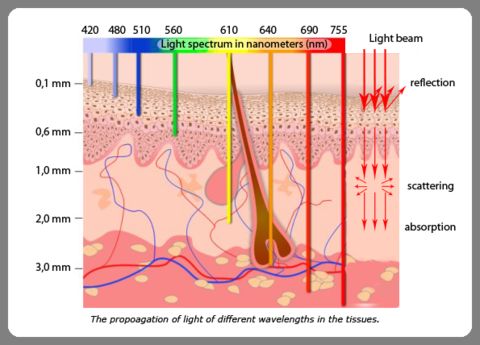

Several LEDs send light at different wavelenghts into the skin, and photodiodes read the scattered light, which is analyzed to perform the authentication.
Plusieurs DELs envoient de la lumière de différentes couleurs dans la peau, et des photodiodes lisent la lumière diffusées, qui est ensuite analysée pour effectuer la reconnaissance.
- (2003) Lumidigm website, now HID (USA)
- (2004 May) Qinetiq (UK, formerly DERA). Skin analyzed in visible range, possibly at a distance. No info available on the web .
- (2005) University at Buffalo (New-York) Center for unified biometrics & sensors (original link is dead) Sarojini Radhakrishnan's thesis
- (2014 Feb) HID buys Lumidigm.
Skin impedance
Bio-Dynamic signature
Signature Bio-Dynamique
(2005 June) Idesia (www.idesia-biometrics.com, dead link) unveils the BDS500:
a reader where you gently place any two fingers from both
hands, one on each contact sensor for just a few seconds.
IDesia scientists have discovered a novel, natural Bio-Dynamic Signature ( BDS ) in humans
- an electro bio signature that is unique to each individual and can be used to accurately
identify any one person from all others.
Unlike most biometric technologies, which use pictures or static bio-signals
to enroll and identify a person, BDS is based on intrinsic electro-biometric dynamic signals
acquired by merely touching a small conductive or metal surface. [copied from their website]
Well, I think they are mainly making an electrocardiogram, it is likely the most important
signal they can read using such a method.
(2005 June) Idesia dévoile le BDS500:
un lecteur où vous placez 2 doigts, un de chaque main, sur chacun des contacts pendant
quelques secondes. Ils l'appellent la "signature bio-dynamique".
Je pense qu'ils font essentiellement un électrocardiogramme, c'est probablement les signaux
du coeur qui sont le principal composant de l'information lue de cette manière.
Hand skin impedance
Pulse-Response biometrics
- (2008) Paper: Authentication Using Pulse-Response Biometrics / Martinovic & als / University of Oxford (local copy)
Biometric Touch Sensing
(2015) Christian Holz and Marius Knaust from Yahoo Labs propose biometric touch sensing, a new approach to representing touch events that enables commodity devices to seamlessly integrate authentication into interaction: From each touch, the touchscreen senses the 2D input coordinates and at the same time obtains biometric features that identify the user. A watch prototype (Bioamp) senses the impedance profile of the user’s wrist and modulates a signal onto the user’s body through skin using a periodic electric signal. This signal affects the capacitive values touchscreens measure upon touch, allowing devices to identify users on each touch.
- (2015) Paper: Biometric Touch Sensing: Seamlessly Augmenting Each Touch with Continuous Authentication (local copy for the records)
- (2015) Presentation: Biometric Touch Sensing
ETRI
- (2008) Paper: Ratiometric Impedance Sensing of Fingers for Robust Identity Authentication / Hyung Wook Noh & als (local copy)